HOW CAN WE HELP YOU? Call 1-800-TRY-CHOP
In This Section
Verbal Consent (Waiver of Documentation)
Frequently called Verbal Consent, the process is more correctly referred to as Informed Consent with Waiver of Documentation. The investigator must obtain consent following the same requirements as written consent but the subject does not sign a consent form. Waiver of documentation of consent is permitted under a limited set of circumstances. The first requirement is that the research is not greater than minimal. This process is sometimes referred to as verbal consent. To waiver documentation of consent, the research must meet the regulatory criteria of 45 CFR 46.117(c) or 21 CFR 50.109(c).
Criteria for Waiver of Documentation of Consent
§46.117(c):
An IRB may waive the requirement for the investigator to obtain a signed consent form for some or all subjects if it finds either:
(i) That the only record linking the subject and the research would be the informed consent form and the principal risk would be potential harm resulting from a breach of confidentiality. Each subject (or legally authorized representative) will be asked whether the subject wants documentation linking the subject with the research, and the subject's wishes will govern;
(ii) That the research presents no more than minimal risk of harm to subjects and involves no procedures for which written consent is normally required outside of the research context; or
Note: This is equivalent to §56.109(c)(1).
(iii) If the subjects or legally authorized representatives are members of a distinct cultural group or community in which signing forms is not the norm, that the research presents no more than minimal risk of harm to subjects and provided there is an appropriate alternative mechanism for documenting that informed consent was obtained.
When a waiver of documentation of informed consent is issued by the IRB the consent process needs to adhere to all of the requirements of consent. In addition, if the study is subject to HIPAA, written HIPAA authorization may still be required unless the study also qualifies for alteration of the requirement for written HIPAA Authorization. The IRB's preference is for the investigator to create consent document using the usual consent template but with a substitution for the usual signature page with one that allows the investigator to document the subject's verbal consent. Examples of situations and options for verbal consent are included below:
-
Consent form using the CHOP consent template without a page for subject or investigator signatures. This option would apply when the basis of waiver was 45 CFR 46.117(c)(1)(i) where the consent form would have been the only link to the research. It could also apply when the plan is to document the consent process place in the research or medical records. This latter situation is risky because it may be difficult to prove during an audit that consent took place.
-
Consent form using the CHOP consent template but substituting the usual signature page with the IRB's documentation of verbal consent page. When assent must be obtained, consent form should also include the page for documentation of verbal assent. A typical scenario for this would be when consent, assent and HIPAA Authorization are obtained over the telephone.
-
Consent form using the CHOP consent template with a page for documentation of verbal consent by the investigator and a stand-alone HIPAA authorization. Some studies will qualify for waiver of documentation of consent but still not qualify for verbal HIPAA authorization. For example, the IRB could waive the requirement for written consent for subjects seen in clinic but the study wouldn't meet the criteria for alteration of HIPAA because it would be practicable to obtain written HIPAA Authorization.
-
Two consent forms, one for written consent and HIPAA Authorization and one for verbal consent. In many studies, some subjects will be seen in-person in clinic and others will be consented over the telephone. The consent of subjects who are seen in clinic include written consent and HIPAA authorization (or verbal consent + written HIPAA Authorization) and the consent of subjects who are enrolled via telephone, would be verbal.
-
Consent script compliant with the regulatory requirements to guide the conversation. The IRB does not encourage the use of scripts but they do remain an option.
This option most often applies to surveys and questionnaires but can also include a specimen collection kit. The questionnaire or specimen collection kit should be accompanied by a letter, webpage or consent form inviting the individual to participate. The letter, webpage instructions or consent form should include:
- The required elements of consent; and
- A statement that completion and return of the questionnaire, web survey, specimen kit, etc. indicates willingness to participate.
This process is sometimes referred to as implied consent, which is not a term recognized by OHRP. They would consider this to be informed consent with waiver of documentation (provided the IRB has waived documentation under 45 CFR 46.117(c)(1)(i), (ii) or (iii)). See OHRP for a discussion about implied consent.
Depending on the circumstances, it may still be appropriate to document that the consent process took place.
Waiver under 45CFR46.117(c)(1)(i)
When a waiver is issued under 45CFR46.117(c)(1)(i) consent should only be documented when the subject requests to be linked to the research. A consent form should be available when using a waiver of documentation under 45CFR46.117(c)(1)(i) in case the subject wishes to be linked. The form of documentation could include any of the following:
- Note written in the study subject's record
- On a consent/assent documentation form with a signature page
- On a consent form with a page for documentation of verbal consent and when applicable, assent and HIPAA Authorization
Waiver under 45CFR46.117(c)(1)(ii)
When a waiver is issued under 45CFR46.117(c)(1)(ii) consent documentation could include any of the following:
- No documentation (strongly discouraged)
- Note written in the study subject's research or medical record
- On a form created specifically for documentation of verbal consent and when applicable, assent and HIPAA Authorization
- On a consent form with a page for documentation of verbal consent and when applicable, assent and HIPAA Authorization
If the plan is to document consent on a copy of the consent form, substitute signature blocks are available in the Special Signatures Page section of the Consent Form Templates page.
Waiver under 45CFR46.117(c)(1)(iii)
When a waiver is issued under 45CFR46.117(c)(1)(iii) consent documentation could be any one of the following:
- Note written in the study subject's research or medical record
- On a form created specifically for documentation of verbal consent and when applicable, assent and HIPAA Authorization
- On a consent form with a page for documentation of verbal consent and when applicable, assent and HIPAA Authorization
If the plan is to document consent on a copy of the consent form, substitute signature blocks are available in the Special Signatures Page section of the Consent Form Templates page.
Please note that these criteria require that an appropriate alternative method is available for documenting that informed consent was obtained.
Example Signature Page to Document Consent Process:
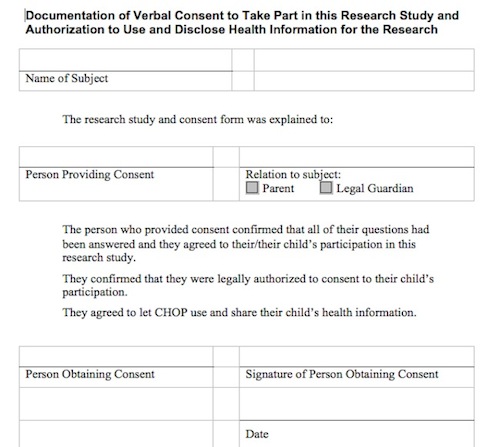
Audio or Videotaping a Verbal Consent
Although audio and videotaping are considered to be minimal risk procedures, CHOP Policy "Recording or Filming of Patients" requires written consent when CHOP patients are involved. Since the requirements of 45 CFR 46.117(c)(1)(ii) specify that a waiver can be granted when the research "involves no procedures for which written consent is normally required outside of the research context" audiotaping and videotaping do not generally qualify. If the participants do not meet the definition of a CHOP patient as defined in the CHOP policy then written consent is not required. This could include physicians and nurses at CHOP or parents of patients.
CHOP legal counsel has concluded that if the consent process for a CHOP patient/subject is taped and then retained as evidence of the consent, then this recording will meet CHOP's requirement for documentation of consent. Under this circumstance, the IRB may waive the requirement for written consent. The details of the requirements are included below and in an email outlining the requirements from CHOP legal counsel.
When can the IRB waive the requirement for written consent for audiotaping for patient-subjects?
If the subject is physically present and is a patient at CHOP, the IRB cannot waive the requirement. This effectively eliminates waivers for videotaping of patient-subjects. If the research involves a telephone interview, then the IRB will consider a request for a waiver. The investigator must do the following:
- Inform the prospective subject that they would like to audiotape the conversation (to comply with state wiretapping laws);
- If the prospective participant agrees, the consent conversation, including the required information about audiotaping must be recorded;
- If the subject consents, the audiotape of the consent conversation must be retained for 6 years (to meet HIPAA and hospital policy).
Waiver of Documentation of HIPAA Authorization
45 CFR 164.164.512:
Uses and disclosures for which an authorization or opportunity to agree or object is not required.
When the research qualifies for a Waiver or Alteration of HIPAA under 45 CFR 164.512(i)(2)(ii) then "A covered entity may use or disclose protected health information without the written authorization of the individual, as described in §164.508, or the opportunity for the individual to agree or object as described in 164.510, in the situations covered by this section, subject to the applicable requirements of this section. When the covered entity is required by this section to inform the individual of, or when the individual may agree to, a use or disclosure permitted by this section, the covered entity's information and the individual's agreement may be given orally."
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the difference between a waiver of documentation of consent and a waiver of consent?
When the IRB grants a waiver of consent, consent is not necessary for enrollment.
When the IRB grants a waiver of documentation of consent, the investigator needs to obtain the subject’s consent but not the subject’s signature to document it. In this case, the investigator can document having obtained consent (e.g. on the verbal consent form or in the study chart).
-
Can I record any individually identifiable private information and obtain a waiver of documentation of consent under 46.117(c)(1)(i)?
In order to waive documentation under (c)(1)(i), all of the data collected must be anonymous which means recorded without any identifying information.
-
If the study is FDA-regulated, can I obtain a waiver of documentation under 46.117(c)(1)(i)?
The FDA regulations mandate that all subjects be identifiable in order to permit an audit of the source documents so there is no FDA equivalent to 46.117(c)(1)(i).
-
Which research procedures can take place and still waive documentation of consent?
To waive the requirement for documentation under 46.117(c)(1)(ii) or 56.109(c)(1), the procedures in the research must be limited to those that don't require written consent as part of clinical care. Examples include: Blood draw, Questionnaires, Chest X-ray, and DXA scan.
-
Why does the IRB require that I have a consent form approved if I have obtained a waiver of documentation of consent?
The IRB must ensure that the subject is provided with the necessary information to make an informed decision about study participation. The waiver of documentation is merely related to the requirement for a subject to sign, and thus document, their consent.
-
When do I need to give the subject an information sheet?
When the IRB waives documentation of consent under (c)(1) or under 50.109(c) of the FDA regulations, it can require the investigator to provide the subject an Information Sheet when the IRB decides that subjects should have some information to refer back to after completion of the study. The contents of the Information Sheet do not need to match those of a consent form but should contain at a minimum:
- The title of the research
- Contact information for the investigator
- An explanation of the purpose of the research
- A description of the procedures
-
What if HIPAA applies to the research, can I still obtain a waiver of documentation of consent?
HIPAA at 45 CFR 164.512 permits oral authorization instead of written authorization provided that the study meets the criteria for alteration or waiver of HIPAA. If the research involves individually identifiable health information, then the investigator must also do one of the following:
- Request an alteration (sometimes referred to as a partial waiver) of Written Authorization, or
- Obtain Written Authorization for use of PHI using a stand-alone HIPAA Authorization